3 Important Javascript Concepts
What is Javascript ?
Javascript, developed in 1995 was built in order to provide an accessible and complementary approach to java. Nowadays, javascript is used as a scripting language that allows users to implement complex features on web pages. This allows us to have dynamically updated content on web pages.
What Are Variables ?
Variables are used in coding to retain data values within your code. When creating a variable, the "var" keyword must be placed in front of the name. The assignment operator "=" is used to assign a value to the variable. A variable can be a :
- Numerical Value
- A string
- A collection of liked items (Array)
- Function
1.1 Variable Declaration
You can declare a variable like this
You can't do this
1.2 Variable Scope
In JavaScript, a variables scope tells us where this variable can be accessed. There are three main types of variables :
- Global - declared in the script tag but is outside of a function. A global variable can be used anywhere within the code.
- Local - declared within the function. A local variable can only be used within the { } block
- Block - declared within a "block" using let keyword. A block variable is only available
Global Variables example
As you can see "var a" was declared outside of the function scope but it is still accessible.
Local Variables example
In this example "var a" has been declared locally inside the " function foo". Using "var a " in "function bar" will result in an error because "var a " is bound to the scope of function.
Block Variables example
As in the example, "let= i" only exists within the {} . This is denoted by the "let" variable type
1.3 Variable types
JavaScript has 6 different primitive variable types. JavaScript has dynamic types. This means that the same variable can be used to hold different data types.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Null | An abstract type. Null is the representation of no value. |
| Undefined | An abstract type. This data type has no assigned value |
| Boolean | A logical value that represents true or false |
| Numbers | Real Numbers |
| Symbols | Any set of character values ex: "John Doe" |
What are Functions?
Functions are reusable blocks of code that have a name, may take in arguments, perform some operations on those arguments,and may return a new value. Having a piece of code that can repeat tasks saves users from writing the same repetitive code statement multiple times.
In this lesson, we will focus on :
- Function Syntax
- Function Parameters
- Function Return Values
2.1 Function Syntax
In order to call a function in JavaScript, you will need to use the keyword "function" and follow it with a "()"
You can create a function like this
In this example, function foo gets called when the button is clicked. Inside function foo, we made an alert to the window console to display a specific message.
You can't call a function like this
2.2 Function Parameters
Parameters are used when you have one or more values that need to be passed to a function. When you have multiple parameters, make sure you separate them with a comma.
It is important to mention that the variable you put into the parameter is local scoped. Meaning that this will not be retained outside of the function call.
Here is an example of how parameters are properly utilized in functions
2.3 Function Return Value
A function can return a value to the script that called upon the function. This is due to the “return” statement.
The return statement is for the most part, placed at the bottom of the function before closing.
Here is an example of how to properly use the return feature
What are Document Object Models?
The Document Object Model , or the DOM for short, is a platform and language-neutral interface that represents the HTML or XML documents. This allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and manipulate content, structure and the style of a particular document.
In this chapter we will primarily focus:
- DOM Document
- DOM Elements
- DOM CSS
3.1 DOM Documents
The document object is a representation of your web page. If you want to access any element on your HTML page, you will have to start with grabbing the document.
All DOM objects may be equipted with any of these members:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Properties | The data values for that object.In some instances these may be read only or read/write depending on the object |
| Methods | These will take parameters and return values and perform a specific function |
| Child objects(nodes) | Nodes that carry their own set of members or even child objects |
| Event handlers | Listens for specific actions and reacts accordingly |
As you can see we will always start the line with "document.(something)". Later on we will see just how much manipulation that can be made with with document
3.2 DOM Elements
Next, we will take a look at elements. In order to access specific elements we are going to have to find them first.
The most common ways of accessing any element are the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
Here is an example on how we to properly fetch elements :
In order to understand what is happening here, it's best to think of the DOM as a tree and everything underneath the tree objects.
Bellow is a diagram representing the DOM and its sub objects
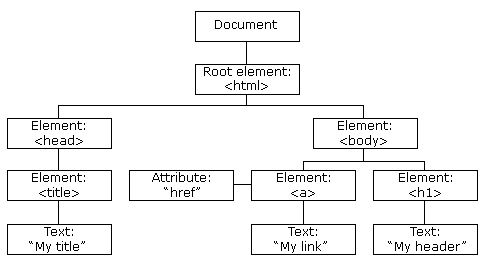
Source : W3C schools
3.3 DOM CSS
We are also able to access and change css elements with the dom object
This is done by accessing the "style" tag